Attention to Tooth Decay in Children!
Tooth Decay in Children: Prevention, Treatment, and Importance of Early Care
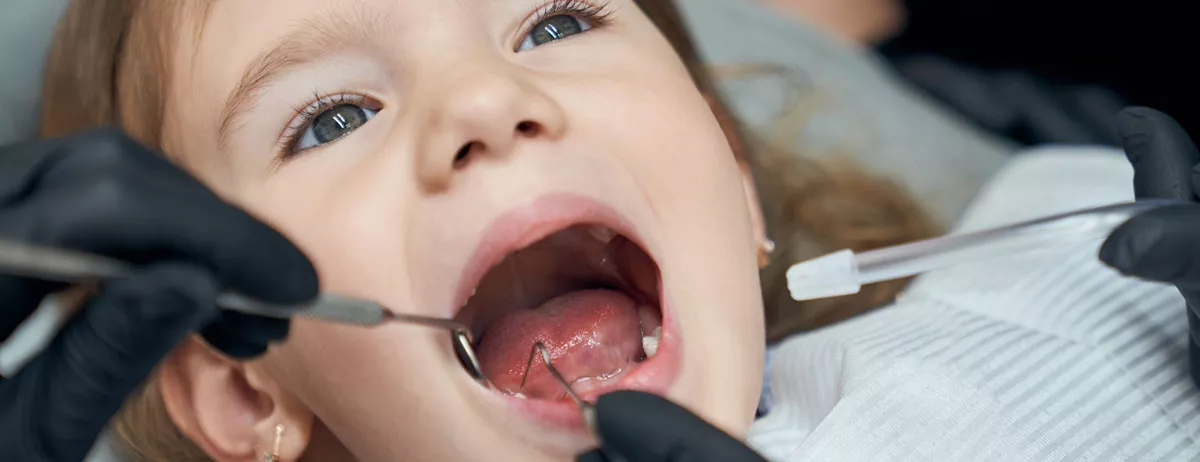
Tooth decay in children, also known as pediatric dental caries or early childhood caries, is a widespread health issue that requires immediate attention. Maintaining healthy baby teeth is essential, as they play a critical role in chewing, speech development, and guiding permanent teeth into place. Neglecting dental caries in children can lead to serious consequences, including pain, infection, difficulty eating, and impaired self-confidence.
Why Is Tooth Decay in Children Important?
Many parents mistakenly believe that decay in baby teeth is not a problem since these teeth will eventually fall out. However, this misconception can cause delays in seeking dental treatment, worsening the condition and increasing the risk of complications. Tooth decay affects children's overall health and quality of life, making early diagnosis and intervention crucial.
Untreated dental caries can cause symptoms such as:
- Toothache and sensitivity
- Difficulty eating or chewing
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Swollen or bleeding gums
- Behavioral changes due to pain or discomfort
Causes of Tooth Decay in Children
Tooth decay is primarily caused by bacterial activity in the mouth that produces acids, which erode the tooth enamel. Factors contributing to tooth decay in children include:
- Poor oral hygiene: Irregular or improper brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup.
- Dietary habits: Frequent consumption of sugary foods and drinks fuels bacteria growth.
- Prolonged bottle feeding: Especially with sugary liquids or milk, which can pool around the teeth.
- Dry mouth: Reduced saliva flow can decrease natural cleaning and protection.
- Genetics: Some children may have a predisposition to weaker enamel.
Symptoms of Tooth Decay in Children
Parents and caregivers should be vigilant for early signs of tooth decay, which may include:
- White spots or chalky areas on the teeth
- Brown or black discoloration
- Visible holes or pits in teeth
- Pain when biting or eating
- Swelling around the tooth or gums
Preventing Tooth Decay in Children
Prevention is the best approach to dental caries. The following practices can significantly reduce the risk:
1. Establish Good Oral Hygiene Habits Early
Begin cleaning your child’s mouth even before teeth emerge by wiping gums with a soft, damp cloth. Once teeth appear, brush twice daily using a child-sized, soft-bristled toothbrush and an appropriate amount of fluoride toothpaste.
2. Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks
Reduce intake of candies, sodas, juices, and other sugary snacks. Encourage healthy alternatives like fruits, vegetables, and water.
3. Avoid Bedtime Bottles with Sugary Liquids
Putting a child to bed with a bottle containing milk, juice, or sweetened liquids increases the risk of “baby bottle tooth decay.” Instead, use water or avoid bottles at bedtime.
4. Regular Dental Check-Ups
Schedule the first dental visit by the child’s first birthday or within six months after the first tooth erupts. Early dental visits allow the dentist to identify and manage risk factors promptly.
5. Fluoride Treatments and Dental Sealants
Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay. Dental professionals may recommend fluoride varnishes or supplements. Sealants can protect the chewing surfaces of molars by sealing grooves where bacteria accumulate.
Treatment Options for Tooth Decay in Children
Depending on the severity and extent of decay, pediatric dentists may recommend various treatments:
- Fillings: For minor cavities, removing decayed tissue and filling the cavity with materials like composite resin restores function and aesthetics.
- Root Canal Treatment: When decay reaches the tooth pulp causing infection, root canal therapy may be necessary even for primary teeth to save them until natural exfoliation.
- Tooth Extraction: Severely damaged teeth that cannot be restored might need extraction. Space maintainers may be used to hold the place for permanent teeth.
- Preventive Treatments: Application of fluoride, professional cleaning, and advice on oral hygiene.
The Role of Pediatric Dentists
Pediatric dentists specialize in children's dental care and are trained to handle the unique needs and behaviors of young patients. They use child-friendly techniques to make dental visits comfortable and stress-free, ensuring positive attitudes towards oral health that last a lifetime.
Importance of Early Intervention
Addressing tooth decay early prevents pain, infections, and potential complications like abscesses or systemic illness. Early treatment also avoids more invasive procedures and preserves the natural dentition, supporting proper speech, nutrition, and development.
Common Myths About Tooth Decay in Children
- “Baby teeth don’t matter because they fall out.” Baby teeth are crucial for chewing, speech, and guiding permanent teeth.
- “Only sugary foods cause cavities.” While sugar is a major factor, poor oral hygiene and other factors also contribute.
- “If a tooth doesn’t hurt, there’s no problem.” Decay can progress silently until advanced stages.
Tips for Parents to Support Children’s Oral Health
- Lead by example: Brush and floss regularly as a family.
- Make brushing fun using songs, games, or colorful toothbrushes.
- Monitor diet and limit sugary snacks.
- Encourage drinking water, especially after meals.
- Ensure regular dental visits and follow professional advice.
Decayed Teeth and Root Canal Treatment in Children
Molars generally appear as the first permanent teeth in children, and this corresponds to the age of 6 on average. It is not possible for children around the age of 6 to properly care for their mouth, but the first permanent teeth must be carefully cared for in order to avoid permanent damage. At this point, even if children have not acquired the habit of brushing their teeth regularly, they should at least rinse their mouth with water after meals. Because tooth decay in children becomes more important after the age of 6, as permanent teeth begin to emerge.
Unless there is a health problem, root canal treatment can be performed on anyone who needs it, including children. If necessary, root canal treatment should be performed to treat caries in order to prevent tooth loss and for children to have a healthier tooth structure.
How to Prevent Tooth Decay in Children?
Tooth decay manifests itself in a complex manner in children, as in every person. Reasons such as inadequate oral care, not having acquired the habit of brushing teeth, and accumulation of food residues between the teeth cause tooth decay in the long term. In general, tooth decay in children is caused by inadequate care. For this reason, in order to prevent tooth decay, children should first be made aware of oral care and inculcated in the habit.
Children brushing their teeth or at least rinsing their mouths with water after consuming foods such as candy and chocolate, as well as after every meal, prevents the formation of tooth decay.
Children and Dental Examination
Tooth decay in children appears over time after it begins to form. The emergence of complaints such as pain and the like indicates that the tooth has already decayed. For this reason, children should be taken to the dentist for regular check-ups starting from the age of 2.5 in order to prevent cavities and provide the necessary caries treatment.